- Most prevalent form of mastitis - causes about 70% of the losses due to mastitis.
- Causes heavy losses due to its prolonged effect throughout lactation.
- The other forms of mastitis (clinical or chronic) develop from this stage.
SYMPTOMS
- No specific symptom seen except a slight decrease in milk production.
- Cannot be normally detected since there is no physical changes in udder or milk.
DETECTION OF SCM
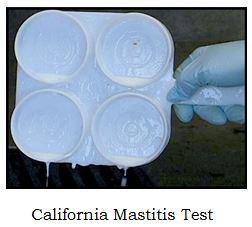
- CMT - Equal quantities of milk and CMT reagent are mixed by rotating, SCM milk will form a gel. CMT reaction may disappear within 20 seconds , readings must therefore be taken fast. Also check each quarter separately.
- CMT may give false positive reaction in very early (less than 10 days) lactation or when animal is almost dry.
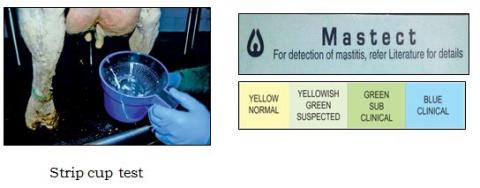
- Strip cup test - Small flakes are present in SCM milk when viewed against a black surface, size of flakes increase with the degree of SCM.
- Paper test - Green colour is indicative of SCM.
- Field mastitis test - Can be carried out like CMT using using concentrated detergent solution instead of CMT reagent.
PREVENTION OF SCM
- All the points mentioned for prevention of ‘clinical mastitis’ are relevant here too.
- Test for the occurrence of SCM in your animals at least once a week.
- Each quarter should be separately tested.
- Newly purchased animals should be tested first for SCM and treated if found positive before mixing them with the herd.
- SCM positive animal (s) should always be milked at the end.
- If animals are tethered in open, change places frequently.
- Ideally, no lubricant should be used during milking. If used, it should be heated daily before use.
TREATMENT
- Consult a veterinarian for proper treatment.
- The chances of curing SCM is much higher than a clinical or chronic case.
- Timely treatment of SCM will also reduce the chances of clinical and chronic cases of mastitis.
Treatment of SCM will greatly reduce losses
