- A highly contagious viral disease
- Spreads through contact, contaminated water, feed and air.
- Disease is rarely fatal for adults, however the milk production, fertility in females and draft power of males are severely impaired for life after recovery from disease.
- Usually fatal in calves.
- Also affects sheep, goat (usually sub-clinically and are maintenance hosts) and pigs, which are amplification hosts (multiplies the virus around 3000 fold).
SYMPTOMS
- Drastic drop in milk production and working capacity (draft animals).
- Fever and serous nasal discharge and excessive salivation.
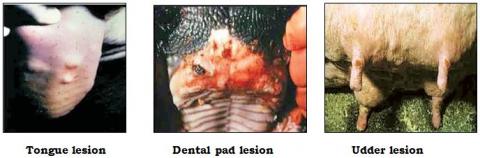
- Vesicles may be seen on tongue, dental pad, lips, gums etc.
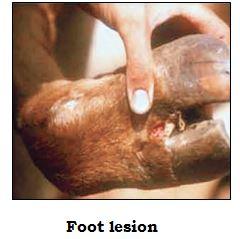
- Vesicle in inter-digital cleft may lead to lameness.
- Lesions on teat may lead to mastitis.
- Loss in condition may persist even after recovery.
PREVENTION
- Get your animals aged 4 months and above vaccinated once in 6 months.
- Infected animals should be immediately separated since all excretions and secretions from infected animals contain the virus.
- All feed and fodder in contact with the infected animal should be destroyed.
- All equipment used should be cleaned and disinfected with 4% sodium carbonate solution or as suggested by a veterinarian.
- Healthy animals should not be handled by persons in contact with infected animals.
- The infected premises should be disinfected with 4% sodium carbonate solution or the disinfectant suggested by a veterinarian.
- Vaccinating sheep, goat and pigs would control the disease to a better extend.
- Informing authorities promptly would enable them initiate control measures at the earliest which will help in limiting the spread of the disease.
MANAGEMENT OF FMD
- Treatment is only symptomatic, the disease will run its course.
- Emollients may be applied on lesions to soothe pain.
- Contact veterinarian for suitable advice.
Vaccinate your animals regularly against FMD to avoid economic losses