- An important viral disease affecting domestic and wild cattle and buffaloes.
- There are three forms : respiratory, genital and encephalitic, the first two are more common. There is a high prevalence of this disease in India.
- Causes abortions, ROP, moderate reduction in milk production and even death in calves. Infection can be transmitted through semen.
SYMPTOMS
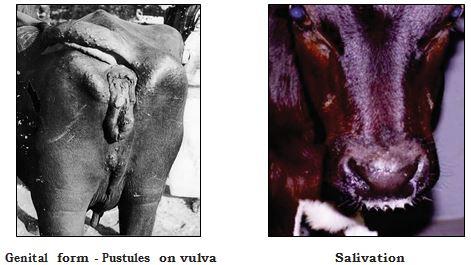
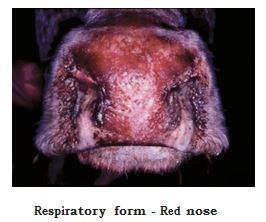
- Coughing, profuse bilateral serous discharge from nostrils and pyrexia.
- Rhinitis, conjunctivitis (one or both eyes) with profuse ocular discharge.
- In genital form, swollen vulva with papules which later become ulcers.
- Abortion is common at 6-8 months of pregnancy.
- Uncomplicated cases of respiratory and genital forms usually resolves in 5-10 days. Infected animals may carry the virus throughout its lifetime.
- The brain may be effected in calves below 6 months causing high mortality.
PREVENTION AND CONTROL
- Purchase new animals only after testing them.
- Induct only negative animals to your farm.
- Though vaccination is a method of prevention, no vaccines are produced in India presently for IBR.
- Consult a veterinarian immediately if the above symptoms are seen to prevent the disease from spreading.
IBR is an emerging disease that needs to be controlled