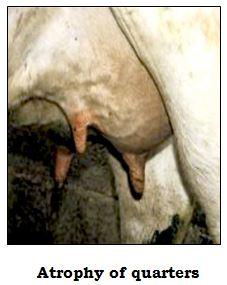
- A persistent infection of udder.
- Exists most of the time in the subclinical form.
- Occasionally can develop into the clinical form before returning to the subclinical.
- This results in hard lumps in the udder.
MAJOR PRE-DISPOSING FACTORS
- Neglected sub- clinical mastitis
- Improper treatment protocol of acute mastitis
- Unhygienic shed
MAJOR SYMPTOMS
- The affected udder may atrophy or may lead to fibrosis leading to decreased or total loss of production in the affected quarter.
- Chances of recovery of chronically affected quarters are very low once atrophy/fibrosis has occurred.

PREVENTION
- Separate the affected cow from rest of the herd since they remain a source of infection for healthy animals. Milk chronically affected cows in the end.
- Screen regularly for sub clinical mastitis and treat positive animals.
- Shed hygiene is of prime importance.
TREATMENT
- Antimicrobial treatment is usually not effective.
- It is better to dispose off such chronically affected animals.
Avoid occurrence of chronic mastitis through timely action
