Articles
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 3:59pm
Methylene Blue Dye Reduction Test for Assessing the Raw Milk Quality
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 3:41pm
MANAGEMENT OF WATER IN DAIRY PLANTS
content:
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 2:49pm
- Ticks transmit diseases like anaplasmosis, theileriosis and babesiosis
- Biting flies transmit diseases like Surra and E fever (see respective chapters).
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 2:49pm
- Worms are parasites that usually live inside the digestive tract of the host, feeding on tissue fluids or blood of the animal. Worms may also be found in lungs, nasal passage, eye etc.
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 2:44pm
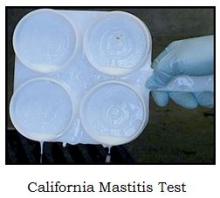
- Most prevalent form of mastitis - causes about 70% of the losses due to mastitis.
- Causes heavy losses due to its prolonged effect throughout lactation.
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 2:43pm
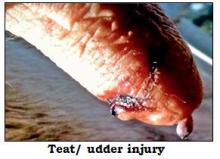
- The most common infectious cause of teat disease in cattle.
- Caused by a virus and not to be confused with cowpox, which is rare.
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 2:42pm
- Traditionally heifers have been thought of as a group free of mastitis which is not true.
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 2:41pm
- Teat warts are caused by virus and heifers are more prone to infection.
- Teat warts may appear as fleshy lumps or they may be of the feathery type.
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 2:38pm
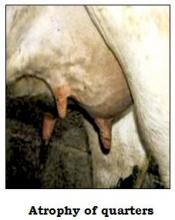
- A persistent infection of udder.
- Exists most of the time in the subclinical form.
- Occasionally can develop into the clinical form before returning to the subclinical.
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 2:36pm
The golden hour: The first hour after calving is the most critical peri
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 2:35pm
- Diarrhoea in calves can occur due to various reasons.
- Calves with diarrhoea lose considerable amounts of water and electrolytes.
Posted on Wednesday, August 6, 2014 - 12:11pm
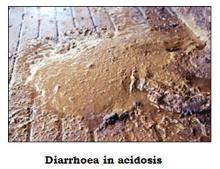
- Acidosis may be clinical or sub- clinical.
- Feeding large quantities of rapidly digestible carbohydrate in a short period of time causes clinical acidosis.
- ‹ previous
- 114 of 117
- next ›